Download English Text book : Click here
Download Malayalam Text book : Click here
Download English Notes : Click here
Click here for Malayalam Note
Chapter – 1
ബിസിനസ്: ബിസിനസ് വ്യാപാരവും വാണിജ്യവും Business Trade and Commerce
ബിസിനസ്സിന്റെ സ്വഭാവവും ലക്ഷ്യവും (NATURE AND CONCEPT OF BUSINESS)
മനുഷ്യപ്രവർത്തനങ്ങളെ രണ്ടായി തരം തിരിക്കാം
1-സാമ്പത്തിക പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ ( Economic Activities )
2-സാമ്പത്തികേതര പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ (Non economic Activities)
സാമ്പത്തിക പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ ( Economic Activities )
പണം നേടുക എന്ന ലക്ഷ്യത്തോടെ ആളുകൾ ഏർപ്പെടുന്ന പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങളാണ് സാമ്പത്തിക പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ
ഉദാ: ഒരു തൊഴിലാളി ജോലിയെടുക്കുന്നത്, ഒരു മാനേജർ ഓഫീസിൽ ജോലി എടുക്കുന്നത്, ഒരു ടീച്ചർ സ്കൂളിൽ ജോലിയെടുക്കുന്നത് ,ഡോക്ടർ ആശുപത്രിയിൽ രോഗികളെ ചികിത്സിക്കുന്നത്.
സാമ്പത്തികേതര പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ (Non economic Activities)
മാനസികമായ സന്തോഷമോ സംതൃപ്തിയോ ലഭിക്കുന്നതിനുവേണ്ടി ഏർപ്പെടുന്ന പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങളെ സാമ്പത്തികേതര പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ എന്ന് പറയാം. ഇത്തരം പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങളുടെ ലക്ഷ്യം പണം നേടുക എന്നുള്ളതല്ല മറിച്ച് മാനസികമായ സന്തോഷമോ സംതൃപ്തിയോ ആർജിക്കുക എന്നുള്ളതാണ്. ഉദാ:കലാകായിക പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ , വീട്ടമ്മ വീട്ടിലുള്ളവർക്ക് ഭക്ഷണം പാകം ചെയ്യുക ,പ്രാർത്ഥിക്കുക ,പാവങ്ങളെ സഹായിക്കുക
വിവിധതരം സാമ്പത്തിക പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ ( Types of Economic Activities:)
സാമ്പത്തിക പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങളെ മൂന്നായി തരം തിരിക്കാം
1 – ബിസിനസ് (Business)
2 – പ്രൊഫഷൻ (Profession)
3 – എംപ്ലോയ്മെൻറ് (Employment)
1 – ബിസിനസ് (Business)
ലാഭം നേടുക എന്ന ലക്ഷ്യത്തോടുകൂടി സാധനങ്ങളും സേവനങ്ങളും ഉത്പാദിപ്പിക്കുകയും വാങ്ങുകയും വിലക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുക എന്ന പ്രവർത്തനത്തിൽ സ്ഥിരമായി ഏർപ്പെടുന്നതാണ് ബിസിനസ്
പ്രത്യേകതകൾ (Features)
- ഇതൊരു സാമ്പത്തിക പ്രവർത്തനമാണ്
- സാധനങ്ങളും സേവനങ്ങളും ഉത്പാദിപ്പിക്കുകയും വാങ്ങുകയോ ചെയ്യുക – ബിസിനസ് ഉപഭോക്താക്കൾക്ക് വിൽക്കുന്നതിനായി സാധനങ്ങൾ സ്വന്തമായി ഉത്പാദിപ്പിക്കുകയോ മറ്റു ഉൽപാദകരിൽ നിന്നും വാങ്ങുകയോ ചെയ്യുന്നു
- സാധനങ്ങളുടെയും സേവനങ്ങളുടെയും വിൽപ്പന അല്ലെങ്കിൽ കൈമാറ്റം – പ്രതിഫലം വാങ്ങി സാധനങ്ങളും സേവനങ്ങളും വിലക്കുകയോ കൈമാറുകയോ ചെയ്യുന്നതാണ് ബിസിനസ്
- സാധനങ്ങളും സേവനങ്ങളും തുടർച്ചയായി വാങ്ങുകയോ വിൽക്കുകയോ ചെയ്യുക – സാധനങ്ങളും സേവനങ്ങളും തുടർച്ചയായി വാങ്ങുകയോ നിൽക്കുകയോ ചെയ്യുന്നതാണ് ബിസിനസ് ഒറ്റത്തവണ വാങ്ങുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നത് ബിസിനസ് അല്ല ഈ പ്രവർത്തനത്തിന് തുടർച്ച വേണം
- ലാഭം നേടുക – ലാഭം നേടുക എന്ന ലക്ഷ്യത്തോടുകൂടി സാധനങ്ങളോ സേവനങ്ങളോ വാങ്ങുകയോ വിൽക്കുകയോ ചെയ്യുന്ന പ്രവർത്തനം മാത്രമേ ബിസിനസായി പരിഗണിക്കുകയുള്ളൂ ലാഭമില്ലാതെ വാങ്ങി വിൽക്കുന്നതിന് ബിസിനസ് എന്ന് പറയില്ല
- വരുമാനത്തിലെ അനിശ്ചിതത്വം – ഭാവിയിൽ എത്ര തുക ലാഭമായി നേടാൻ കഴിയുമെന്നത് അനിശ്ചിതമാണ് ബിസിനസിൽ എപ്പോഴും നഷ്ടം സംഭവിക്കാനുള്ള സാധ്യതയുണ്ട്
- നഷ്ട സാധ്യത ഘടകം – ഏത് ബിസിനസിലും നഷ്ടം ഉണ്ടാവാനുള്ള സാധ്യതയുണ്ട് ഈ സാധ്യത പാടെ ഒഴിവാക്കാനാവില്ല
2- പ്രൊഫഷൻ (Profession)
പ്രത്യേക പരിജ്ഞാനവും പരിശീലനവും ആവശ്യമുള്ളതും വ്യക്തിപരമായ സേവനം ചെയ്യേണ്ടതുമായ ജോലിയാണ് പ്രൊഫഷൻ ഉദാഹരണം വക്കീൽ, എൻജിനീയർ, ചാർട്ടേഡ് അക്കൗണ്ടൻറ്, ഡോക്ടർ
പ്രത്യേകതകൾ (Features)
- പ്രൊഫഷൻ ചെയ്യുന്നതിനുവേണ്ടി പ്രത്യേകമായ അറിവും കഴിവും പരിശീലനവും ആവശ്യമാണ്
- ഒരു ഒരു പ്രൊഫഷൻ ചെയ്യുന്നതിന് ആ പ്രൊഫഷൻ ചെയ്യുന്നവരുടെ കൂട്ടായ്മയിൽ അംഗത്വം നിർബന്ധമാണ് (Membership)
- പ്രൊഫഷൻ ചെയ്യുന്നതിന് പകരമായി ഫീസാണ് അവര് ഈടാക്കുന്നത്
- എല്ലാ പ്രൊഫഷൻ ചെയ്യുന്നവരും അവരുടെ അസോസിയേഷൻ രൂപപ്പെടുത്തിയിട്ടുള്ള നിയമാവലി പിന്തുടരാൻ നിർബന്ധിതരാണ്.
3- എംപ്ലോയ്മെൻറ് (Employment)
ശമ്പളം അല്ലെങ്കിൽ കൂലി കൈപ്പറ്റി ഒരു കരാറിന്റെ അടിസ്ഥാനത്തിൽ ഒരു തൊഴിലാളി തൊഴിൽ ദാതാവ് ഏൽപ്പിക്കുന്ന ജോലി ചെയ്യുന്നതാണ് എംപ്ലോയ്മെൻറ്.
പ്രത്യേകതകൾ (Features)
- ഇവിടെ ഒരു തൊഴിലാളി തൊഴിൽദാതാവ് ബന്ധം നിർബന്ധമാണ്
- തൊഴിലെടുക്കുന്ന ആളും തൊഴിൽ ദാദാവും തമ്മിലൊരു കരാർ ഏർപ്പെട്ടിരിക്കുന്നു
- തൊഴിലാളിക്ക് ശമ്പളം അല്ലെങ്കിൽ കൂലി പകരമായി ലഭിക്കുന്നു.
വിവിധതരം ബിസിനസ് പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ(Types of Business Activity)
A – വ്യവസായം (Industry ) B – വാണിജ്യം (Commerce)
A – വ്യവസായം(Industry )
വിഭവങ്ങളെ ഉപയോഗപ്രദമായ സാധനങ്ങൾ ആക്കി മാറ്റുന്ന സാമ്പത്തിക പ്രവർത്തനമാണ് വ്യവസായം
വ്യവസായങ്ങളെ മൂന്നായി തരം തിരിക്കാം
1 – പ്രാഥമിക (Primary)
2 – ദ്വിതീയം (Secondary)
3 – തൃതീയം (Tertiary)
1 – പ്രാഥമികം വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ (Primary Industries)
പ്രകൃതിയിൽ നിന്നും നേരിട്ട് വിഭവങ്ങൾ എടുത്തു കൊണ്ട് പ്രകൃതിവിഭവങ്ങളുടെ ഖനനവും ഉൽപാദനവും കൂടാതെ സസ്യ ജീവജാലങ്ങളുടെ പുനരുല്പാദനം വികസനം എന്നിവയുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട വ്യവസായമാണ് പ്രാഥമിക വ്യവസായം. ഇവയെ രണ്ടായി തരം തിരിക്കാം
- പ്രകൃതി ജന്യ വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ (Extractive Industries)
മണ്ണ് ജലം മുതലായവയിൽ നിന്നും ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങൾ ഖനനം ചെയ്തെടുക്കുകയോ ഉത്പാദിപ്പിക്കുകയോ ചെയ്യുന്നതിൽ ഏർപ്പെട്ടിരിക്കുന്ന വ്യവസായമാണിത് Ex:ഖനനം കൃഷി, മീൻപിടുത്തം ,വേട്ടയാടൽ
- ജൈവശാസ്ത്രപരമായ വ്യവസായം (Genetic Industries)
സസ്യങ്ങൾ മൃഗങ്ങൾ എന്നിവയുടെ ഉൽപാദനം പരിപാലനം എന്നിവയുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട വ്യവസായമാണിത്. കന്നുകാലി പരിപാലനം കോഴി വളർത്തൽ കാർഷിക നഴ്സറി
2 – ദ്വിതീയ വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ (Secondary Industries)
പ്രാഥമിക വ്യവസായത്തിൽ നിന്നും ഉല്പാദിപ്പിച്ച വിഭവങ്ങൾ വീണ്ടും ഉൽപാദന പ്രക്രിയയ്ക്ക് വിധേയമാക്കുകയോ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ അന്തിമ ഉപയോഗത്തിനുള്ള ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങൾ ആക്കി മാറ്റുകയോ ചെയ്യുന്ന വ്യവസായമാണിത്.
ഇതിനെ വീണ്ടും രണ്ടായി തരം തിരിക്കാം
- ഉൽപാദന വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ (Manufacturing Industries)
അസംസ്കൃത വസ്തുക്കൾ അന്തിമ ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങൾ ആക്കി മാറ്റുന്ന വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ ആണിത്
തടിയെ ഫർണിച്ചർ ആക്കുക,പരുത്തിയ വസ്ത്രങ്ങൾ ആക്കുക, ഇരുമ്പായി സ്റ്റീൽ ആക്കുക
ഇതിനെ വീണ്ടും നാലായി വിഭജിക്കാം
- അനലിറ്റിക്കൽ (Analytical)-ഒരു അസംസ്കൃത വസ്തുവിൽ നിന്നും വിവിധ ഘടകങ്ങൾ വേർതിരിച്ചെടുക്കുന്ന വ്യവസായം.Ex: എണ്ണ ശുദ്ധീകരണ ശാല
- സിന്തറ്റിക്കൽ (Synthetical) – വിവിധ ഘടകങ്ങളെ സംയോജിപ്പിച്ച് പുതിയ ഒരു ഉൽപ്പന്നം ഉണ്ടാക്കുന്നു. സിമൻറ് വ്യവസായം
- പ്രോസസിംഗ് (Processing) – ഒരു ഉൽപ്പന്നം ഉല്പാദിപ്പിക്കുന്നത് വിവിധ ഘട്ടങ്ങളിലുള്ള പ്രക്രിയകളിലൂടെ കടന്നുപോയിട്ടാണ് എങ്കിൽ അത്തരം വ്യവസായങ്ങളെ പ്രോസസിംഗ് വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ എന്ന് പറയും. പഞ്ചസാര വ്യവസായം
- അസംബ്ലി (Assembling) -വിവിധ ഘടകങ്ങൾ കൂട്ടിച്ചേർത്തുകൊണ്ട് പുതിയ ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങൾ നിർമ്മിക്കുന്ന വ്യവസായം കമ്പ്യൂട്ടർ കാർ ടിവി
- നിർമ്മാണ വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ (Construction Industries)
റോഡുകൾ പാലങ്ങൾ അണക്കെട്ടുകൾ കെട്ടിടങ്ങൾ മുതലായവയുടെ നിർമ്മാണത്തിൽ ഏർപ്പെട്ടിരിക്കുന്ന വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ
3 – തൃതീയ വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ (Tertiary Industries)
പ്രാഥമിക വ്യവസായങ്ങൾക്ക് പിന്തുണ സേവനങ്ങൾ നൽകുന്ന വ്യവസായങ്ങൾ ആണിത്. ഉദാ: ഗതാഗതം ബാങ്കിംഗ് ഇൻഷുറൻസ് വെയർഹൗസിംഗ് കമ്മ്യൂണിക്കേഷൻ
B – വാണിജ്യം (Commerce )
ഒരു ഉൽപ്പന്നം ഉൽപാദകന്റെ കയ്യിൽ നിന്നും ഉപഭോക്താവിന്റെ കയ്യിലേക്ക് കൈമാറ്റം ചെയ്യുന്നതിന് ഇടക്ക് ഉണ്ടാകുന്ന വ്യക്തിപരവും സ്ഥല സ്ഥലപരവും സമയ പരവുമായ തടസ്സങ്ങളെയെല്ലാം നീക്കം ചെയ്യുന്നതുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങളുടെ ആകെ തുകയാണ് വാണിജ്യം. വാണിജ്യത്തിൽ 1 – കച്ചവടം , 2 – കച്ചവട സഹായങ്ങൾ എന്നിവ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു.
1 – കച്ചവടം (Trade)
സാധനങ്ങൾ വാങ്ങുകയും വിലക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്ന പ്രവർത്തനമാണ് കച്ചവടം. ഉത്പാദകരിൽ നിന്നും ഉപഭോക്താവിലേക്ക് സാധനങ്ങൾ എത്തിക്കാൻ കച്ചവടം സഹായിക്കുന്നു. വ്യക്തിപരമായ തടസ്സം നീക്കുന്നു
വിവിധ തരം കച്ചവടങ്ങൾ (Types of Trade)
1-ആഭ്യന്തര കച്ചവടം (Internal Trade)
ഒരു രാജ്യത്തിൻറെ ഭൂമിശാസ്ത്രപരമായ അതിർത്തിക്കുള്ളിൽ നടക്കുന്ന സാധനങ്ങളുടെയും സേവനങ്ങളുടെയും വാങ്ങലും വില്പനയും ആണ് ആഭ്യന്തര കച്ചവടം. ഇതിനെ മൊത്ത വ്യാപാരം ചില്ലറ വ്യാപാരം എന്നിങ്ങനെ രണ്ടായി തരം തിരിക്കാം
- മൊത്ത വ്യാപാരം (Wholesale Trade ) –ഉൽപാദകരിൽ നിന്നും വലിയ അളവിൽ സാധനങ്ങൾ വാങ്ങി കുറഞ്ഞ അളവിൽ ചില്ലറ വ്യാപാരികൾക്ക് വിൽക്കുന്നതാണ് മൊത്ത വ്യാപാരം
- ചില്ലറ വ്യാപാരം (Retail Trade ) – മൊത്ത വ്യാപാരികളിൽ നിന്നും സാധനങ്ങൾ വാങ്ങി വളരെ ചെറിയ അളവിൽ ഉപഭോക്താക്കൾക്ക് വിൽക്കുന്നതാണ് മൊത്ത വ്യാപാരം
2 – വിദേശ വ്യാപാരം (Foreign Trade)
വാങ്ങുന്ന ആളും വിൽക്കുന്ന ആളും രണ്ട് വ്യത്യസ്ത രാജ്യങ്ങളിലാണെങ്കിൽ ഇതിനെ വിദേശ വ്യാപാരം എന്ന് പറയും. ഇതിനെ മൂന്നായി തരം തിരിക്കാം
- ഇറക്കുമതി കച്ചവടം (Import Trade ) – മറ്റൊരു രാജ്യത്തുനിന്നും സാധനങ്ങൾ വാങ്ങുന്നതാണ് ഇറക്കുമതി
- കയറ്റുമതി കച്ചവടം (Export Trade )-മറ്റൊരു രാജ്യത്ത് സാധനങ്ങൾ വിൽക്കുന്നതാണ് കറ്റുമതി കച്ചവടം
- എൻട്രി പോട്ട് കച്ചവടം(Entrepot Trade) – മറ്റു രാജ്യങ്ങളിലേക്ക് കയറ്റുമതി ചെയ്യുന്നതിനായി സാധനങ്ങൾ ഇറക്കുമതി ചെയ്യുന്നതാണ് എൻട്രി കച്ചവടം
2 – കച്ചവട സഹായങ്ങൾ (Auxiliaries to Trade )
1-ഗതാഗതം – അസംസ്കൃത വസ്തുക്കൾ ഉൽപാദന കേന്ദ്രങ്ങളിലേക്ക് എത്തിക്കുന്നതിനും അന്തിമ ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങൾ ഉപഭോഗസ്ഥലങ്ങളിലേക്ക് എത്തിക്കുന്നതിനും ഗതാഗതം സഹായിക്കുന്നു ഇത് സ്ഥലപരമായ തടസ്സം നീക്കുന്നു
2-ബാങ്കിംഗ് – ബിസിനസ്സിന്റെ പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾക്ക് പണം ആവശ്യമാണ് ബാങ്കുകൾ ബിസിനസിന് ആവശ്യമായ പണം നൽകുന്നു ബാങ്കിംഗ് പണപരമായ തടസ്സം നീക്കുന്നു
3-ഇൻഷുറൻസ് – തീപിടുത്തം വെള്ളപ്പൊക്കം ഭൂകമ്പം തുടങ്ങിയ കാരണങ്ങൾ മൂലം ബിസിനസിന് നഷ്ടങ്ങൾ സംഭവിക്കാം ഈ നഷ്ടസാധ്യതകൾക്കെതിരെ ഇൻഷുറൻസ് ബിസിനസിന് സംരക്ഷണം നൽകുന്നു ഇൻഷുറൻസ് നഷ്ട സാധ്യത തടസ്സം നീക്കുന്നു
4-വെയർ ഹൗസിംഗ്– ഉല്പാദിപ്പിച്ച ഉൽപ്പ ന്നങ്ങൾ ഉപഭോക്താവിനെ വിൽക്കപ്പെടുന്നതുവരെ സൂക്ഷിച്ചുവെക്കുന്ന സംവിധാനമാണ് ബെയർ ഹൗസിംഗ്. സമയപരമായ തടസ്സം നീക്കുന്നു
5-പരസ്യം– ഒരു ഉൽപ്പന്നത്തെ സംബന്ധിച്ച വിവരങ്ങൾ ഉപഭോക്താക്കൾക്ക് നൽകുന്നതിനും അവരെ സാധനങ്ങൾ വാങ്ങുവാൻ പ്രേരിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിനും പരസ്യം സഹായിക്കുന്നു. ഇത് അറിവ് പരമായ തടസ്സം നീക്കുന്നു.
ബിസിനസിന്റെ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങൾ
- ലാഭം നേടുക
- മാർക്കറ്റിൽ ബിസിനസിന്റെ സാന്നിധ്യം നിലനിർത്തുക
- ഇന്നോവേഷൻ -പുതിയ ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങളും പുതിയ വ്യാപാര രീതികളും നടപ്പിൽ വരുത്തുക
- ഉൽപാദനക്ഷമത കൈവരിക്കുക
- ബിസിനസിന്റെ കയ്യിലുള്ള വിഭവങ്ങൾ പരമാവധി കാര്യക്ഷമമായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുക
- ബിസിനസ്സിലുള്ള മാനേജർ കഴിവും അവരുടെ വികാസവും ഉറപ്പുവരുത്തുക
- തൊഴിലാളികൾക്ക് തൊഴിൽ പുരോഗതി ഉറപ്പുവരുത്തുക.
ബിസിനസിൽ ലാഭത്തിനുള്ള പങ്ക്
- ബിസിനസ് ചെയ്യുന്നവർക്കുള്ള വരുമാന മാർഗ്ഗമാണ് ലാഭം
- ബിസിനസ്സിന്റെ തുടർന്നുള്ള വികസനത്തിനുള്ള സാമ്പത്തിക ഉറവിടമാണ്.
- പാപം ബിസിനസിന്റെ കാര്യക്ഷമതയുടെ അളവുകോലാണ്
- നഷ്ടസാധ്യത ഏറ്റെടുക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള പ്രതിഫലമാണ് ലാഭം
ബിസിനസിലെ നഷ്ട സാധ്യതകൾ (Business Risks)
അനിശ്ചിതമോ അപ്രതീക്ഷിതമോ ആയ സംഭവങ്ങൾ മൂലം ഒരു ബിസിനസിന് വേണ്ടത്ര ലാഭം ലഭിക്കാതിരിക്കുകയോ നഷ്ടം സംഭവിക്കുകയോ ചെയ്യുന്നതിനെയാണ് ബിസിനസ് നഷ്ട സാധ്യതകൾ എന്ന് പറയുന്നത്.
നഷ്ട സാധ്യതയുടെ കാരണങ്ങൾ (Causes of Business Risks)
1-പ്രകൃതിദത്ത കാരണങ്ങൾ –തീപിടുത്തം പ്രളയം ഭൂകമ്പം എന്നിവ
2-മാനുഷിക കാരണങ്ങൾ-മനുഷ്യരുടെ ഇടപെടൽ കാരണം ബിസിനസിന് ഉണ്ടാകുന്ന നഷ്ട സാധ്യതകൾ. ഉദാഹരണം ജീവനക്കാരുടെ അശ്രദ്ധ സമരം ലഹള കാര്യക്ഷമതയില്ലായ്മ
3-സാമ്പത്തിക കാരണങ്ങൾ -മാർക്കറ്റിൽ ഉണ്ടാവുന്ന വിലയിലും ഡിമാന്റിലും ഉണ്ടാകുന്ന മാറ്റങ്ങൾ മത്സരം തുടങ്ങിയവ
4 -രാഷ്ട്രീയപരമായ കാരണങ്ങൾ- രാഷ്ട്രങ്ങളുടെ പോളിസികളിൽ ഉണ്ടാവുന്ന മാറ്റങ്ങൾ, നികുതി നിരക്കുകളിൽ ഉണ്ടാകുന്ന മാറ്റങ്ങൾ ലൈസൻസ് പോളിസി തുടങ്ങിയവ
5- മാനേജ്മെൻറ് കാരണങ്ങൾ– മാനേജ്മെന്റിന്റെ തെറ്റായ തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ, വികലമായ പ്ലാനിങ്, റിസർച്ച് ആൻഡ് ഡെവലപ്മെൻറ് ഇല്ലായ്മ തുടങ്ങിയവ
ഒരു ബിസിനസ് ആരംഭിക്കുമ്പോൾ പരിഗണിക്കേണ്ട (Starting a Business: Basic factors)
- ഏത് തരത്തിലുള്ള ബിസിനസ് വേണമെന്ന് തെരഞ്ഞെടുപ്പ്
- സംരംഭത്തിന്റെ വലിപ്പം
- ഉടമസ്ഥാവകാശത്തെ സംബന്ധിച്ച തെരഞ്ഞെടുപ്പ്
- ബിസിനസ് ആരംഭിക്കാൻ പോകുന്ന സ്ഥലത്തെ സംബന്ധിച്ച തെരഞ്ഞെടുപ്പ്
- ബിസിനസിന് ആവശ്യമായ പണം കണ്ടെത്തുന്നുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ
- ബിസിനസ് തുടങ്ങുന്നതിന് ആവശ്യമായ അടിസ്ഥാന കാര്യങ്ങൾ അവർ പൊരുത്തുക
- പ്ലാൻറ് ലേ ഔട്ട് – ബിസിനസ് പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നതിന് ആവശ്യമായ മിഷനറികളും ഉപകരണങ്ങളും കാര്യക്ഷമമായി സംവിധാനിക്കുക
- ബിസിനസിന്റെ പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ നടത്തുന്നതിന് ആവശ്യമായ തൊഴിലാളികളെ കണ്ടെത്തുക
- ബിസിനസ്സിന്റെ നികുതിപരമായ കാര്യങ്ങൾ പ്ലാൻ ചെയ്യുക
- ബിസിനസ് പ്രവർത്തിച്ചു തുടങ്ങുക
All human beings require different types of goods and services to satisfy their needs. To satisfy such needs people are undertaking certain activities by way of production and selling of goods and services.Business is a major economic activity in all modern societies as it is concerned with the production and sale of goods and services required by people.
Human activities can be classified into two categories:
1. Economic Activities and 2.Non-Economic Activities.
- Economic Activities: Activities which are undertaken by people with the object of earning money are known as economic activities. The purpose of economic activities is to earn money which is used for further creation of wealth or assets.
Eg. Production of goods in a factory, lawyer, working in a school, doctor, clerk, daily worker etc…
- Non-Economic Activities: The activities which are undertaken by an individual with a motive of getting psychological satisfaction or out of sentiments or out of religious obligation are known as non-economic activities.
Eg.: Praying, social service, production for self consumption, charity etc…
| Economic Activities | Non-Economic Activities |
| To earn money or money’s worth | For personal or psychological satisfaction |
| It can be measured in terms of money | It cannot be measured in monetary terms |
| Money is the reward | Mental satisfaction is the reward |
Types of Economic Activities: Economic activities can be divided into three categories:
1. Business 2. Profession 3.Employment
2 – Business: Activities which are related to production or purchase and sale or distribution of goods or service with the main objective of earning profit come under business. It should be on a regular basis.
Eg: Manufacturing, mining, farming, trading, fishing etc..
Characteristics of Business/ Features of Business
- Economic activity: All business activities are considered as an economic activity because its main aim is to earn money in the form of profit.
- Dealing goods or services: Business involves transfer or exchange of goods or services for value. Goods may be of consumer goods ( for direct use. Eg.clothes, food item …) or capital goods (like machinery, tools…..).
- Regularity in dealing: An isolated transaction cannot make a business unit. When transactions are repeatedly performed, it is considered as business.
- Profit earning: The first and foremost purpose of business is to earn profit. Profit is the return on capital employed.
- Sale, transfer or exchange: Business must involve sale, transfer or exchange of goods and services directly or indirectly.
- Uncertainty and business risk: No one can predict the future of a business with certainty. In every business there is a chance of loss or deduction of profit. It is called business risk. 2 – Profession: Profession refers to an occupation which requires specialized knowledge, skill and training. Those engaged in professions are known as professionals. Eg.: Lawyer, Doctor, Engineer, CA…
Features:
- A profession requires specialized knowledge, training and skill. Eg. A Doctor must possess MBBS, Lawyer possess LLB etc.
- The membership of the professional body is a must. Eg. CA must obtain membership from ICAI, Doctor obtain membership from Medical Council of India, Lawyer from Bar Council …..
- They charge fee in return of their services.
- Every professional must follow certain rules and regulations enforced by the professional body. It is known as code of conduct.
3 – Employment: Employment refers to that type of economic activity in which people engage in some work for others regularly and get salary/wages in return of their services.
Eg.: officer, clerk, factory worker, government servants ….
Features:
- There must exist employer-employee relationship.
- There must be a service contract between employer and employee.
- Employees get salary or wages for their services.
- Regularity in service.
Comparison or Distinction between Business, Profession and Employment
| Basis | Business | Profession | Employment |
| 1. Commencement | Decision of entrepreneur | Membership of professional body | Appointment letter |
| 2. Nature of work | Production or purchase
and sale of goods or services |
Rendering expert service | Performing the job assigned by the employer |
| 3. Qualifications | No minimum qualification | Professional
qualification and training |
Prescribed by the employer |
| 4. Capital | Depends on the nature &size of business | Limited capital | No capital |
| 5. Risk | High risk | Less risk | No risk |
| 6. Transfer of interest | Possible | Not possible | Not possible |
| 7. Objective/Return | Profit | Fees | Salary |
| 8.Code of conduct | No code of conduct | Laid down by the professional body | Laid down by the employer. |
Classification of Business
Business activities may be broadly classified into two broad categories – Industry and Commerce.
INDUSTRY
- A. Industry: Industry involves production or processing of goods used for consumption or for further production.
Types of Industry: Primary ,Secondary ,Tertiary Extractive Genetic Manufacturing Construction Analytical Synthetical Processing Assembling
- Primary Industry; Primary industries are associated with extraction of natural resources and reproduction of living organisms like plants, animals and birds. It is classified into two: Extractive industry: Which engage in extraction of something from natural sources or from nature. The products extracted are wither directly consumed or are used as raw materials for further production. Eg. Fishing, mining, oil exploration etc. Genetic industries: They are engaged in activities like rearing or breeding of animals, birds and plants. Eg. Agriculture, dairy farming for milk, poultry farming for egg and meat, Floriculture for flowers pisciculture for fish etc.
- Secondary Industries: It deals with materials extracted at the primary stage. These industries either process the material or produce goods. It is further classified in to two; Manufacturing industries: They engage in converting raw materials into finished goods. The products manufactured may either be consumer goods or capital goods. Eg. Producing steal, make furniture, making butter etc.
It may be divided into following categories:
- Analytical industry: In it the main products or rawmaterial is divided into various sub products. Eg. Petroleum industry.
- Synthetic Industry: In it one main product is made from various raw materials. Eg. Soap, paint …
- Processing Industry: In it different stages are involved in transferring raw material in to finished goods. Eg. Textile industry.
- Assembling Industry: In it different parts of the products are purchased from te market and assembled to make a complete product. Eg. Cycle industry. Construction industries; They engaged in construction of dams, bridged, airports etc. The products of these industries are immovable, labour intensive and which are used mostly for public welfare. 3 – Tertiary industries; They concern with providing services that support the primary industries and secondary industries. Eg. Transport, banking, insurance etc.
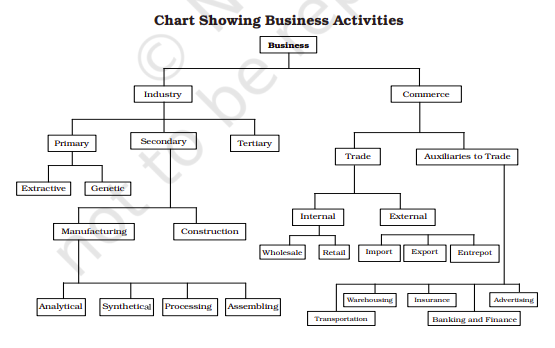
COMMERCE
Commerce is concerned with the buying, selling and distribution of commodities and it is an organized system for the exchange of goods and services in between the businessman and the customers. It is also concerned with the marketing aspects of business, i.e. supply of right type of goods to the right persons, at the right time and at the right price. Thus commerce includes trade and aids to trade.
Definition – Commerce can be defined as the sum total of all those activities which are involved in the removal of hindrances in the process of exchange of goods.
Types of Trade
Internal/home/domestic trade , External/Foreign/International trade ,Whole sale ,Retail ,Export ,Import ,Entrepot
- Home trade: When trade taken place within the boundaries of a country
a. Wholesale trade: Buying goods in bulk and sell them in the smaller quantities to retailer.
b. Retail trade: Buying goods in small quantity from wholesaler or producer and sell them to consumers. - Foreign Trade: When trade taken place beyond the boundaries of a nation is called external trade.
Export: When goods are sold to a foreign country.
Import: When goods are purchased from a foreign country
Entrepot : When goods are imported for export to other countries.
Functions of Commerce –
- Removal of Hindrance of Person: It refers to the lack of contact between the producers and customers. Here the trader acts as an intermediary among them and customers are able to find out the products which they are wanted from the market.
- Removal of Hindrance of Place: It is a common problem that the producers and customers are in distant places, hence the commodities should be transferred from the production centre to the hands of customers. This problem can be solved by the system of commerce by means of transport, packing and insurance.
- Removal of Hindrance of Risk: Goods and properties of business are subject to various risk such as fire, theft, damage etc., and they have to be protected by insuring the goods and properties.
- Removal of Hindrance of Time: There may be a gap between the production and consumption as the production is carried out in anticipation of future demands.Therefore, it becomes necessary to store the goods until they are sold. This problem can be solved by warehousing.
- Removal of Hindrance of Knowledge: Advertising helps in the removal of hindrance of knowledge among the buyers.
- Removal of Hindrance of Finance: The problem of finance can be handled by banks, which form part of commerce. It will also help the businessman in exchange of money between different persons at different places.
Aids to trade: Activities which assist trade are called aids to trade or auxiliaries to trade. It includes banking, transportation, communication, insurance, advertising, warehousing, packaging etc.
⮚ Banking Service: Business activities cannot be undertaken unless funds are available for its various needs. Banking services provides finance facility to business and thus it removes the hindrances of finance.
⮚ Transport and Communication: Production of goods generally takes place in particular locations. But these goods are required for consumption in different part of the country. Various modes of transport and communication facilities helps in the movement of goods and removes the hindrance of place in the exchange of goods.
⮚ Insurance: Business involves various types of risks. Insurance provide protection in all these situations. Thus the hindrance of risk is removed through insurance.
⮚ Advertising: It is practically impossible for producers and traders to contact each other and every customer. For sales promotion, information about the product must reach potential buyers. Advertising helps in this situation. The hindrance of knowledge or information is removed through advertising.
⮚ Warehousing: Usually goods are not sold or consumed immediately after production. They are held in stock to be available as and when required. The function of storage is called warehousing and it removes the hindrance of time in the exchange process.
Objectives of Business:
- Earning Profit: Business activities are primarily undertaken to earn profit. Profit is an indicator of the performance of the business during its operation period.
- Market standing: It refers to capture the market share. The business can survive only if there is demand for its goods and services. So it must aim at satisfaction and winning of customers.
- Innovation: To innovate means to introduce something new into the market. It includes new products, new method of production, new method of distribution etc. Eg. Introduction of lap top, changes in mobile phone, conversion of traditional photography to digital, direct marketing etc.
- Productivity: It is ascertained by comparing the value of output with the value of inputs. Every business must aim at greater productivity through the best use of available resources.
- Efficient utilization of physical and financial resources: Any business require physical resources like plants, machines, materials… and financial resources. The business enterprise must aim at acquiring these resources according to their requirements and use them efficiently.
- Manager performance and development: Business need managers to conduct and coordinate business activity, therefore improve managers performance and development is an important objective of every business.
- Improve workers performance and attitude: Every enterprise must aim at improving its workers performance. It should also try to ensure a positive attitude on the part of workers.
- Social responsibility: Social responsibility refers to the obligation of business firms to contribute resources for solving social problems and work in a socially desirable manner.
Business Risk
Business risk means chance of incurring losses or less profit than expected. It is found in every business. Risk arises due to uncertainty about the future events.
Causes of Business Risk:
- Natural causes: It includes heavy rain, famine, earthquake, fire, drought, Tsunami etc.
- Human causes: It includes theft, strike, lockout, negligence and carelessness, riots etc.
III. Economic causes: It includes change in demand and price, market conditions, competitions, trade depression etc.
- Political causes: It includes changes in government policies regarding expert import, taxation, licensing policy, ideology of political parties etc.
- Management causes: It include poor planning, absence of research and development, mismanagement etc.
Starting a Business- Basic Factors:
Some of the basic factors, which must be considered by anybody who is to start the business, are as follows:
- Selection of line of business: It means nature and type of business to be undertaken. 2. Size of the business: Size or scale of operation is another important decision to be taken at the start of the business.
- Choice of form of ownership: The business organization may take the form of a sole proprietorship, partnership or a joint stock company. Each form has its own merits and demerits.
- Location of business: Availability of raw meterial, labour, power, water and other various services are important factors while making a choice of location.
- Finance: Proper financial planning must be done before selecting form of business. 6. Physical facilities: Availability of physical facilities like buildings, machines, supportive services …. are very important factor to be considered.
- Plant layout: It means the physical arrangement of machines and equipment needed to manufacture a product.
- Work force: Plans should be made to bout the number of employees, their competence and how they will be trained and motivated.
- Tax planning: The founder of the business has to consider in advance the tax liability under various tax laws and its impact on business.
- Launching the enterprise: After consider the above factors, the business man can go ahead with the actual launching of the enterprise.
History of Trade and Commerce
Trade and commerce have played a vital role in making India to evolve as a major actor in the economic world in ancient times. Commercial cities like Harappa and Mohenjodaro were founded in the third millennium B.C. The civilisation had established commercial connections with Mesopotamia and traded in gold, silver, copper, coloured gemstones, beads, pearls, sea shells, terracotta pots, etc.There were diverse types of coins and weighing practices which used to vary from place to place.
Indigenous Banking System
As economic life progress, metallic money had been introduced which in turn accelerated the economic activities. Documents such as Hundi and Chitti were in use for carrying out transactions in which money passed from hand to hand.
Hundi as an instrument of exchange, it involved a contract which warrant the payment of money, the promise or order which is unconditional and capable of change through transfer by valid negotiation.
Indigenous banking system played a prominent role in lending money and financing domestic and foreign trade with currency and letter of credit. With the development of banking, people began to deposit precious metals with lending individuals functioning as Bankers or Seths.
Rise of Intermediaries
Intermediaries played an important role in the promotion of trade. They helped the producers especially in foreign trade. They consist of commission agents, brokers and distributors for wholesale and retail of goods.
Transport
Transport by land and water was popular in the ancient times. Roads as a means of transportation had assumed key importance in the process of growth especially in inland trade.
The northern trade route from Bengal to Taxila was an example for the same.
Maritime trade was another important branch of global trade network. Muziris (ancient harbor) in Malabar Coast (near to the present-day Cochin) has a long history of international maritime trade.
Calicut was also an important market for Chinese to acquire items like frankincense, pepper (black gold), pearls, cotton etc.
Pulicat on Coromandel Coast (Tamil Nadu) was a major port in the 17th century. Textiles were the principal export item from Pulicat to Southeast Asia.
Trading Communities
Different trading communities strengthened in ancient India and they dominated trade in different parts of the country. Some of them are as follows:
Punjabi and Multani – Merchants in northern region
Bhats – Gujarat and Rajastan
Mahajan – Western India
Chatt – South India
Merchant Corporations
They were autonomous corporations (guilds) formed to protect the interests of the traders. These corporations were organised on formal basis, framed their own rules and code of conduct, which even kings were supposed to accept and respect. The guild chief directly dealt with the king or tax collectors and settled the market toll (tax) on behalf of its fellow merchants at a fixed sum of money.
Major Trade Centres
- Pataliputra – Patna in Bihar today. Commercial town and major centre for export of stones.
- Peshawar – City in Pakistan. Very popular for export of wool and for the import of horses. Major transactions between India, China and Rome in the first century.
- Taxila – City in Pakistan, also called Thakshashila. Popularly known as the city of financial and commercial banks.
- Indraprastha – Located in the region of present-day New Delhi. It was a commercial junction where most routes leading the east, west, south and north converged (joined).
- Mathura – City in UP. It was an emporium of trade and people here subsisted (lived) on commerce. Many routes from South India touched Mathura and Broach (Bharuch in Gujarat).
India begins to Reindustrialise
After independence, the process of rebuilding the Indian economy have been started. As a part of this the first five year plan was implemented in 1952. Due importance was given to the establishment of modern industries, modern technological and scientific institutes, space and nuclear programs.
To overcome the problems of lack of capital, rise in population, huge expenditure on defence, inadequate infrastructure etc. India relied heavily on borrowings from foreign sources and finally, agreed to economic liberalization in 1991.
The Indian economy is one of the fastest growing economies in the world today. The high growth sectors have been identified, which are likely to grow at a rapid pace and the recent initiatives of the Government of India such as ‘Make in India’, ‘Skill India’, ‘Digital India’, Foreign Trade Policy 2015-20 etc. is expected to help the economy in terms of exports and imports and trade balance.