Finance is the lifeblood of business. The term finance means money or fund. The requirement of funds by business to carry out its various activities is called business finance. Every business, irrespective of its nature, type, size needs finance for its operation. Without finance there is no business. The word finance refers to requirement of money as and when it is needed. In fact the use of money for an activity is known as finance. This chapter gives a clear picture about the various sources and types of business finance.
Types of Business Finance:-
The financial needs of a business can be categorised as follows:
- Fixed capital requirements: In order to start business, funds are required to purchase fixed assets like land and building, plant and machinery, and furniture and fixtures. This is known as fixed capital requirements of the enterprise. The funds required in fixed assets remain invested in the business for a long period of time.
- Working Capital requirements: A business needs funds for its day to day operation. This is known as working Capital requirements. Working capital is required for purchase of raw materials, to pay salaries, wages, rent and taxes.
CLASSIFICATION OF SOURCES OF FUNDS
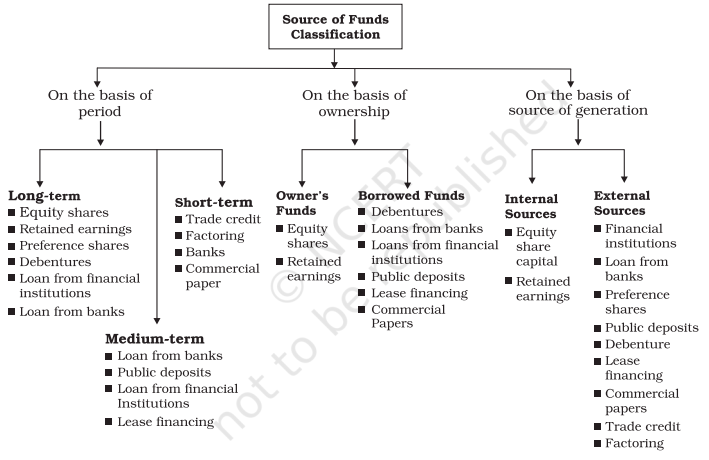
Period Basis: –
On the basis of period of time, the business finance may be divided into:-
- Long Term Finance: – Finance required for a long period of time is known as long term finance. Usually it is for more than five years. This finance is required for the purchase of fixed assets. On the other hand long term fund are required for financing capital expenditure. They are also known as Fixed Capital.
- Medium Term Finance: – Business firm needs funds for comparatively shorter period of time say 1 to 5 years. This is known as medium term finance. This finance is generally used for increasing production capacity, introduction of new products, renewal or modernization of machinery, making huge advertising campaign etc…
- Short Term Finance: – It refers to requirement of finance for a period not exceeding one year. Short term funds are needed for meeting day to day expenses of the business, like purchase of raw material, payment of wages, salary etc… This fund is also known as Working Capital.
Ownership Basis: –
On the basis of ownership, the sources can be classified into ‘owner’s funds’ and ‘borrowed funds’.
Owners’ Fund: – Owners’ Fund represents the amount of capital provided by owners and amount of profit retained in the business. The features of owned fund are:-
- It is the risk capital
- It is the permanent source of capital
- No security is required for owned fund
Borrowed Fund: – Borrowed fund refers to funds mobilized from outsiders. It includes issue of Debentures, loans from financial institutions etc…. Following are the features of the borrowed fund:-
- These funds are mobilized for a fixed period of time
- These fund requires security
- It must repaid after a fixed period
- It must required to pay interest regularly
Source of Generation Basis: –
On the basis of source of generation business finance is categerised into: –
Internal sources and External sources.
Internal Sources: – Internal sources of funds are those that are generated from within the business.
External sources: – External sources of funds include those sources that lie outside an organisation.
SOURCES OF FINANCE:-
A business can raise funds from various sources. A brief description of various sources, along with their advantages and limitations is given below.
1 – Retained Earnings or Ploughing Back of Profit:-
Retained earnings refer to undistributed profit. It is in the form of reserve and surplus. It is a method of internal financing. A portion of company’s net profit is not distributed but is retained for reinvestment purpose, is called retained earnings. Generally it is used for financing expansion and modification of business.
Merits: –
1. No costs: – No costs in the form of interest, dividend, advertisement and prospects.
2. No charges on assets: – The Company does not have to mortgage its assets.
3. Growth and expansion: – Growth and expansion of business is possible by reinvesting the retained profits.
4. Goodwill: – The market price of the company share will increase
Demerit: –
1. Uncertain Source: – It is uncertain source of fund because it is available only when profits are high.
2. Dissatisfaction among shareholder: – Retained profits cause dissatisfaction among the shareholder because they get low dividend.
2 – Trade Credit: –
Trade credit is the credit extended by one trader to another for the purchase of goods and services. Trade credit facilitates the purchase of supplies without immediate payment. Such credit appears in the records of the buyer of goods as ‘sundry creditors’ or ‘accounts payable’.
Merits: –
1. Trade credit is a convenient and continuous source of funds;
2. Trade credit may be readily available.
3. Trade credit needs to promote the sales of an organisation;
4. It does not create any charge on the assets of the firm while providing funds.
Limitations: –
1. Only limited amount of funds can be generated through trade credit;
2. It may lead to overtrading-bulk stocking of goods.
3 – Factoring:-
Factoring refers to management of account receivables. Factoring means direct selling of the account receivables of business enterprise to a factoring firm (factor), which is specialized in the management of account receivables. . Ex : SBI Factors and Commercial Services Ltd., Canbank Factors Ltd., Foremost Factors Ltd
The ‘factor’ renders various services which include:-
- Discounting of bills (with or without recourse) and collection of the client’s debts: – Under this, the receivables on account of sale of goods or services are sold to the factor at a certain discount. There are two methods of factoring —recourse and non-recourse. Under recourse factoring, the client is not protected against the risk of bad debts. On the other hand, the factor assumes the entire credit risk under non-recourse factoring i.e., full amount of invoice is paid to the client in the event of the debt becoming bad.
- Providing information about creditworthiness of prospective clients.
Merits of factoring:-
- Obtaining funds through factoring is cheaper than other means financing
- The client is able to meet his liabilities promptly as and when these arise.
- Ensures a definite pattern of cash inflows from credit sales;
- It provides security for a debt that a firm might otherwise be unable to obtain;
- It does not create any charge on the assets of the firm;
- The client can concentrate on other functional areas of business.
Demerit: –
- This source is expensive when the invoices are numerous and smaller in amount;
- The advance provided by the factor firm is generally available at a higher interest rate
- The factor is a third party to the customer who may not feel comfortable while dealing with it.
4 – Lease Financing
A lease is a contractual agreement whereby one party i.e., the owner of an asset grants the other party the right to use the asset in return for a periodic payment. In other words it is a renting of an asset for some specified period. The owner of the assets is called the ‘lessor’ while the party that uses the assets is known as the ‘lessee’.
The lessee pays a fixed periodic amount called lease rental to the lessor for the use of the asset.
Merits: –
- It enables the lessee to acquire the asset with a lower investment;
- Simple documentation makes it easier to finance assets;
- Lease rentals paid by the lessee are deductible for computing taxable profits;
- It provides finance without diluting the ownership or control of business;
- The lease agreement does not affect the debt raising capacity of an enterprise;
- The risk of obsolescence is borne by the lesser.
Limitations: –
- A lease arrangement may impose certain restrictions on the use of assets.
- The normal business operations may be affected in case the lease is not renewed;
- It may result in higher payout obligation
- The lessee never becomes the owner of the asset.
5 – Public Deposits
The deposits that are raised by organisations directly from the public are known as public deposits. Rates of interest offered on public deposits are usually higher than that offered on bank deposits. Public deposits can take care of both medium and short-term financial requirements of a business.
Merits
- The procedure is simple and does not contain restrictive conditions as are generally there in a loan agreement;
- Cost of public deposits is generally lower than the cost of borrowings from banks and financial institutions;
- Public deposits do not usually create any charge on the assets of the company.
- As the depositors do not have voting rights, the control of the company is not diluted.
Limitations
- New companies generally find it difficult to raise funds through public deposits;
- It is an unreliable source of finance as the public may not respond when the company needs money;
- Collection of public deposits may prove difficult, particularly when the size of deposits required is large.
6 – Commercial Paper (CP)
Commercial Paper emerged as a source of short term finance in our country in the early nineties. Commercial paper is an unsecured promissory note issued by a firm to raise funds for a short period, varying from 90 days to 364 days. The amount raised by CP is generally very large. As the debt is totally unsecured, the firms having good credit rating can issue the CP.
Merits
- A commercial paper is sold on an unsecured basis and does not contain any restrictive conditions;
- As it is a freely transferable instrument, it has high liquidity;
- It provides more funds compared to other sources.
- Companies can park their excess funds in CP thereby earning some good return on the same.
Limitations
- Only financially sound and highly rated firms can raise money through commercial papers.
- The size of money that can be raised through commercial paper is limited
- Commercial paper is an impersonal method of financing. As such if a firm is not in a position to redeem its paper due to financial difficulties,
- Extending the maturity of a CP is not possible.
Issue of Shares:-
The capital of a company divided into a large number of equal units or parts. Each such unit is called as Shares. These shares are offered to public. The person who subscribe shares are called Shareholders, they are the owners of the company.. The aggregate value of shares is known as Share Capital of the company. A share is the interest of a person in the share capital of a company. Share capital is the ownership capital.
Types of Shares: – There are basically two types of shares, they are:-
- Equity Shares or Ordinary Shares
- Preference Shares
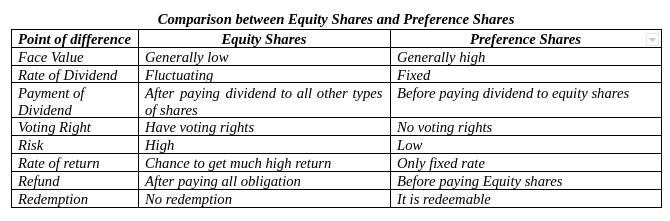
Equity Shares:-.
Equity share is the common security issued under owner’s capital. It is the most important source of raising long term capital. The equity shares are those shares which do not carry any preferential rights in the payment of dividend or repayment of capital. At the time of winding up also capital of equity shareholders is returned only after every claim has been settled.
Generally the rate of dividend is not fixed on equity shares. It may vary from time to time. If the profit is insufficient, equity shareholders may not get any dividend at all. On the other hand, if the company is successful and level of profit is high, equity shareholders may enjoy very high return. Thus they bear high risk.
Equity shareholders are the real owners of the company. They have voting right and the right of control and management of the company.
Features of Equity Shares:-
- Equity shareholders are the primary risk bearers in the company.
- It provide risk capital to the company
- Equity shares enable the holders to get much higher return during the prosperity.
- Equity shareholders have the right to control and management the company
Advantages of Equity Shares:-
- It provides permanent capital to the company.
- No need of security
- It is possible to raise large amount of capital
- The equity shareholder is entitled to the right of vote
- It does not bear fixed rate of dividend
- It facilitate a higher rate of return to be earned with the help of borrowed capital
Disadvantages of Equity Shares:-
- A company has to complete a number of legal formalities to issue equity shares
- The issue of equity share depends up on market condition
- The rate of dividend is fluctuating
- It cannot be returned
Preference Shares:-
The Preference Shares are refers to those shares which have some preferential rights over equity shares. The preferential rights are:-
- The right to get dividend at a fixed rate when a it is declared by the company
- The right to claim repayment of capital in the event of winding up of the company
That means Preference Shares are those shares which get preference over equity shares in respect to the payment of dividend and the repayment of capital during the winding up.
Features of Preference Shares:-
- Preference shareholders get fixed rate of dividend before paying dividend to equity shareholders
- Companies do not offer any security against preference shares
- The preference shareholders do not get voting rights in the company
Types of Preference Shares:-
- Cumulative Preference Shares:- In case of cumulative preference shares, if dividend is not paid due to inadequate profit in a particular year, the amount of dividend will accumulate and will have to be paid out of profit of future years.
- Non-Cumulative Preference Shares:- The preference shares on which dividend does not get accumulated are known as non-cumulative preference shares. That means fixed rate of dividend is payable only when the company is earning profit
- Participating Preference Shares: – The preference shares which get share in the surplus profit of the company after paying all obligations are known as participating preference shares.
- Non-Participating Preference Shares:- the preference shares which have no rights to participate in the surplus profit is called as non-participating preference shares
- Convertible Preference Shares:- The preference shares which get converted into equity shares on expiry of a fixed period of time are known as convertible preference shares
- Non-Convertible Preference Shares: – The preference shares which do not get converted into equity shares are known as non-convertible preference shares.
Advantages of Preference Shares:-
- It help to collect large amount of capital
- Dividend to preference share is paid only when the company earn profit
- The preference shareholders do not carry any voting right. It is best to equity shareholders
- No security is needed
- There are different types of preference shares
Disadvantages of Preference Shares:-
- From the point of view of the company, the dividend on preference share is fixed liability
- From the point of view of shareholders, there is no voting right
- Dividend is not treated as expenses for Taxation Law is concerned , hence tax liability may increase
- The shareholder get dividend only when the company earn profit.
Debentures or Bonds:-
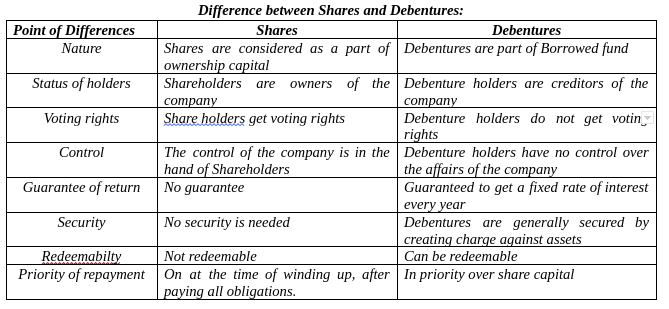
Debentures are common securities issued under borrowed capital. Debentures are instrument for raising long term debt capital. When a company decided to raise loan from the public, the amount of loan is divided into units of equal value. These units are known as debentures.
A debenture is document or certificate issued by a company under its seal as an acknowledgement of its debts. Debentures are the creditorship securities; hence debenture holders are creditors of the company.
Features of Debenture:-
- Debenture is part of borrowed fund.
- It carry a fixed rate of interest
- It is compulsory to pay interest on debenture even if there is no profit
- Debenture requires security or charge against assets of the company
- Debenture holders are creditors; they have no voting rights
Types of Debentures:-
- Secured or Mortgaged Debentures:- These are debentures which are secured by a charge on the assets of the company
- Unsecured or Naked or Simple Debenture:- Such debentures are unsecured and do not carry a charge on the assets of the company
- Convertible Debentures:- these are debentures which can be converted into equity shares of the company after expiry of a specified period
- Non-Convertible Debentures:- These debentures cannot be converted in to equity shares
- Registered Debentures: – In case of registered debentures, the name and details of debenture holder are entered in the register of the company. They can be transferred by executing transfer deed
- Unregistered or Bearer Debentures: – The company does not maintain any register of holders of these debentures. They are transferable by mere delivery.
- First Debentures: Debentures that are repaid before other debentures are repaid are known as first debentures.
- Second debentures: are those which are paid after the first debentures have been paid back.
Advantages of Debentures:-
- The cost of raising debentures is comparatively less
- It provide greatest security to the investors
- It guarantee a fixed rate of interest
- Interest paid on debenture is tax deductible expense.
- Debenture provide funds to the company for a long period without dilution of control of equity shareholders
Disadvantages of Debentures:-
- Payment of interest is a fixed commitment to the company
- Debenture holders do not enjoy any voting rights
- There is a need of charge on assets of the company as security
- Debenture issue is not possible for companies with unstable future earnings
Commercial Banks:-
Commercial Banks give loan and advances to business in the form of cash credit, overdraft loans and discounting of Bill. Rate of interest on loan is fixed.
Merits:
1. Timely financial assistance: – Commercial Bank provides timely financial assistance to business.
2. Secrecy: – Secrecy is maintained about loan taken from a Commercial Banks.
3. Easier source of funds: This is the easier source of funds
Demerits:
1. Short or Medium term finance: Funds are not available for a long time.
2. Charge on assets: Required source security of assets before a loan is sanctioned.
Loans from Financial Institution:-
A number of financial institutions are set up by the government with the main object of promoting industrial finance. They are called as public financial institution. Some of the most important among them are: – IDBI, IFCI, ICICI, IRBI, SFC, UTI, LIC etc……
Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)
State Financial Corporations (SFC)
Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI)
Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI)
State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDC)
Unit Trust of India (UTI)
Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd
Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC)
Merits: –
1. Long-term Finance: Financial Institution provides long term finance which is not provided by commercial banks
2. Managerial Advice: They provide financial, managerial and technical advice to business firm.
3. Easy installments: Loan can be made in easy installments.
Demerits;-
- More time Consuming: The procedure for granting loan is time consuming due to rigid criteria and many formalities.
- Restrictions: Financial Institution place restrictions on the company’s autonomy of management
INTERNATIONAL FINANCING
In addition to the sources discussed above, there are various avenues for organisations to raise funds internationally. With the opening up of an economy and the operations of the business organisations becoming global, Indian companies have an access to funds in global capital market. Various international sources from where funds may be generated include:
1. Commercial Bank: Commercial Bank all over the world provide foreign currency loan for business. Standard Chartered is a major source of foreign currency loan to the Indian industry.
2. International Agencies and development Bank: Many number of international agencies and development Bank e.g. IFC, ADB provide long term loan.
3. International Capital Markets: Different ways of raising finance from international capital market are:-
A) Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds (FCCB’s): Foreign currency convertible bonds are equity linked debt securities that are to be converted into equity or depository receipts after a specific period. FCCB’s are listed and traded in foreign stock exchanges. FCCB’s are very similar to the convertible debentures issued in India.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE CHOICE OF THE SOURCE OF FUNDS
An effective appraisal of various sources must be instituted by the business. . These factors should be analysed together while making the decision for the choice of an appropriate source of funds.
1- COST: – Cost of Owned fund is more than borrowed fund
2 TIME PERIOD:-Long term finance is raised through shares and debentures.
Short term finance is raised through trade credit, commercial paper, etc.
3 RISK – There is least risk on Equity shares as the capital need not be repaid.
But in case of loan, interest has to be paid
4-CONTROL – Issue of equity shares may lead to dilution of control but debt involves no dilution of control.
5-STABILTY OF EARNINGS: – Stability of earnings is important because loan should be raised only when earning are sufficient.
6-CREDIT WORTHINESS: – The firm having more creditworthiness goes to borrowed fund
7 TAX IMPACT: – Interest on debenture is tax deductible. Dividend is not tax deductible.